# 翻转二叉树
题目链接🔗
想要翻转二叉树,只需要交换每个节点的左右子节点即可。
这道题目使用层序遍历、前序遍历和后序遍历都可以,唯独中序遍历不方便,因为中序遍历会把某些节点的左右孩子翻转了两次!
# 递归法
以前序遍历递归:

class Solution { | |
public: | |
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) { | |
if (root == nullptr) return root; | |
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中 | |
invertTree(root->left); // 左 | |
invertTree(root->right); // 右 | |
return root; | |
} | |
}; |
# 迭代法
# 深度优先遍历
以前序遍历迭代:
class Solution { | |
public: | |
TreeNode* inverTree(TreeNode* root) { | |
stack<TreeNode*> st; | |
if(root != nullptr) st.push(root); | |
while(!st.empty()) { | |
TreeNode* node = st.top(); | |
if(node != nullptr) { | |
st.pop(); | |
if(node->right) st.push(node->right); | |
st.push(node); | |
st.push(nullptr); | |
if(node->left) st.push(node->left); | |
} | |
else { | |
st.pop(); | |
node = st.top(); | |
st.pop(); | |
swap(node->left, node->right); | |
} | |
} | |
return root; | |
} | |
}; |
# 广度优先遍历
层序遍历交换左右子子树:
class Solution { | |
public: | |
TreeNode* inverTree(TreeNode* root) { | |
queue<TreeNode*> que; | |
if(root) que.push(root); | |
while(!que.empty()) { | |
int size = que.size(); | |
for(int i = 0; i < que.size(); i++) { | |
TreeNode* node = que.front(); | |
que.pop(); | |
swap(node->left, node->right); | |
if(node->left) que.push(node->left); | |
if(node->right) que.push(node->right); | |
} | |
} | |
return root; | |
} | |
}; |
# 对称二叉树
题目链接🔗
判断对称二叉树要比较的不是左右节点。
要比较的是根节点的左右子树是不是互相翻转的,比较的是两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等。
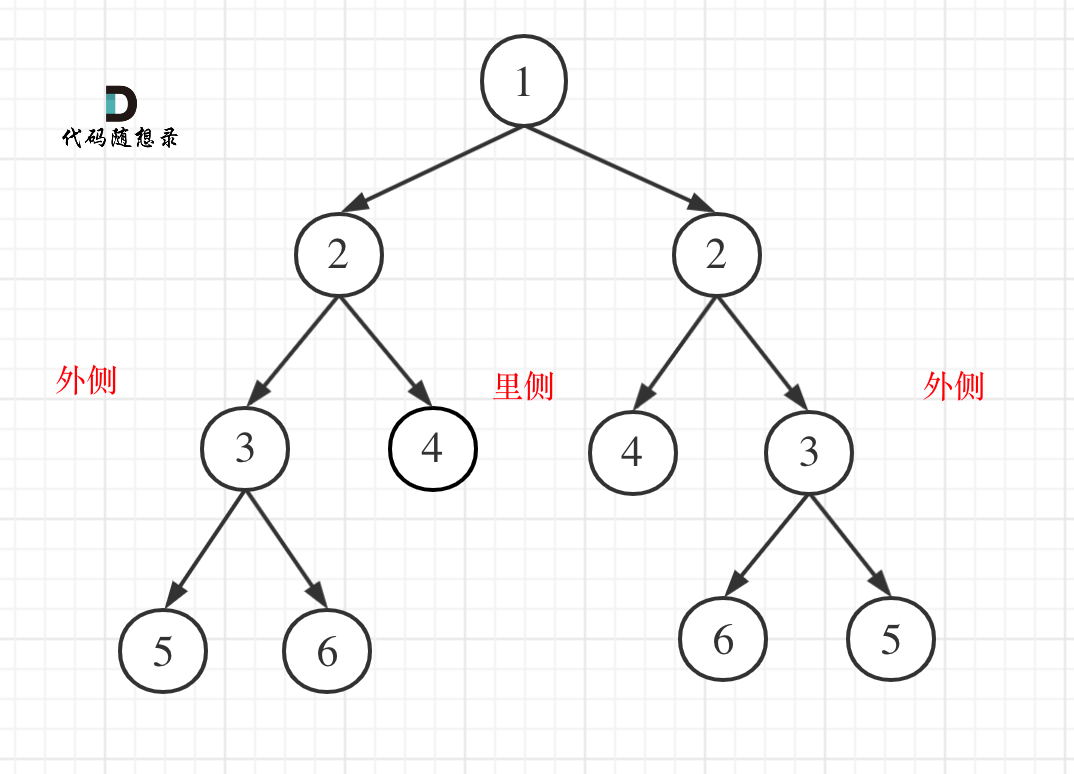
本题只能用后序遍历,因为要通过递归函数的返回值来判断两个子树的内侧节点和外侧节点是否相等。
因此要遍历两棵树而且要比较内侧和外侧的节点,一个树的遍历顺序是左右中,一个树的遍历顺序是右左中。
但都可以理解是后序遍历。
# 递归法
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
因为我们要比较的是根节点的两个子树是否是相互翻转的,进而判断这个树是不是对称树,所以要比较的是两个树,参数自然也是左子树节点和右子树节点。
返回值自然是 bool 类型。
- 确定终止条件
考虑两个节点为空的情况和数值比较。
节点为空的情况有三种:
- 左节点为空,右节点不空,return false
- 左节点不空,右节点为空,return false
- 左右节点都为空,return true
此时排除掉了节点为空的情况,剩下的就是数值不相同的情况:
- 左右都不为空,数值不相同,return false
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
单层递归的逻辑就是处理 左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况。
- 比较二叉树外侧是否对称:传入的是左节点的左孩子,右节点的右孩子。
- 比较内侧是否对称,传入左节点的右孩子,右节点的左孩子。
- 如果左右都对称就返回 true ,有一侧不对称就返回 false 。
class Solution { | |
public: | |
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) { | |
// 首先排除空节点的情况 | |
if (left == nullptr && right != nullptr) return false; | |
else if (left != nullptr && right == nullptr) return false; | |
else if (left == nullptr && right == nullptr) return true; | |
// 排除了空节点,再排除数值不相同的情况 | |
else if (left->val != right->val) return false; | |
// 此时就是:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况 | |
// 此时才做递归,做下一层的判断 | |
bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right); // 左子树:左、 右子树:右 | |
bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left); // 左子树:右、 右子树:左 | |
bool isSame = outside && inside; // 左子树:中、 右子树:中 (逻辑处理) | |
return isSame; | |
} | |
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { | |
if (root == nullptr) return true; | |
return compare(root->left, root->right); | |
} | |
}; |
# 迭代法
迭代法和递归思路一致,可以使用队列来比较两个子树。
但迭代法不是层序遍历。

class Solution { | |
public: | |
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { | |
if (root == nullptr) return true; | |
queue<TreeNode*> que; | |
que.push(root->left); // 将左子树头结点加入队列 | |
que.push(root->right); // 将右子树头结点加入队列 | |
while (!que.empty()) { // 接下来就要判断这两个树是否相互翻转 | |
TreeNode* leftNode = que.front(); que.pop(); | |
TreeNode* rightNode = que.front(); que.pop(); | |
if (!leftNode && !rightNode) { // 左节点为空、右节点为空,此时说明是对称的 | |
continue; | |
} | |
// 左右一个节点不为空,或者都不为空但数值不相同,返回 false | |
if ((!leftNode || !rightNode || (leftNode->val != rightNode->val))) { | |
return false; | |
} | |
que.push(leftNode->left); // 加入左节点左孩子 | |
que.push(rightNode->right); // 加入右节点右孩子 | |
que.push(leftNode->right); // 加入左节点右孩子 | |
que.push(rightNode->left); // 加入右节点左孩子 | |
} | |
return true; | |
} | |
}; |
# 二叉树最大深度
题目链接🔗
# 递归法
本题可以用前序遍历也可以用后序遍历。前序求的是深度,后序求的是高度。
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从
根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从 0 开始还是从 1 开始) - 二叉树节点的高度:指从
该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从 0 开始还是从 1 开始)
根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度。
前序遍历代码:
class solution { | |
public: | |
int result; | |
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) { | |
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中 | |
if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) return ; | |
if (node->left) { // 左 | |
getdepth(node->left, depth + 1); | |
} | |
if (node->right) { // 右 | |
getdepth(node->right, depth + 1); | |
} | |
return ; | |
} | |
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { | |
result = 0; | |
if (root == nullptr) return result; | |
getdepth(root, 1); | |
return result; | |
} | |
}; |
后序遍历代码:
class solution { | |
public: | |
int getdepth(TreeNode* node) { | |
if (node == nullptr) return 0; | |
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左 | |
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右 | |
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中 | |
return depth; | |
} | |
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { | |
return getdepth(root); | |
} | |
}; |
# 迭代法
层序遍历模板题。
class solution { | |
public: | |
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { | |
if (root == nullptr) return 0; | |
int depth = 0; | |
queue<TreeNode*> que; | |
que.push(root); | |
while(!que.empty()) { | |
int size = que.size(); | |
depth++; // 记录深度 | |
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { | |
TreeNode* node = que.front(); | |
que.pop(); | |
if (node->left) que.push(node->left); | |
if (node->right) que.push(node->right); | |
} | |
} | |
return depth; | |
} | |
}; |
# 二叉树的最小深度
题目链接🔗
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点(左右孩子都为空的节点)的最短路径上的节点数量。
# 递归法
如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。
最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
所以,求二叉树的最小深度和求二叉树的最大深度的差别主要在于处理左右孩子不为空的逻辑。
后序遍历代码
class Solution { | |
public: | |
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) { | |
if (node == NULL) return 0; | |
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左 | |
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右 | |
// 中 | |
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点 | |
if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) { | |
return 1 + rightDepth; | |
} | |
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点 | |
if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) { | |
return 1 + leftDepth; | |
} | |
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth); | |
return result; | |
} | |
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { | |
return getDepth(root); | |
} | |
}; |
前序遍历代码
class Solution { | |
private: | |
int result; | |
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) { | |
// 函数递归终止条件 | |
if (node == nullptr) { | |
return; | |
} | |
// 中,处理逻辑:判断是不是叶子结点 | |
if (node -> left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) { | |
result = min(result, depth); | |
} | |
if (node->left) { // 左 | |
getdepth(node->left, depth + 1); | |
} | |
if (node->right) { // 右 | |
getdepth(node->right, depth + 1); | |
} | |
return ; | |
} | |
public: | |
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { | |
if (root == nullptr) { | |
return 0; | |
} | |
result = INT_MAX; | |
getdepth(root, result); | |
return result; | |
} | |
}; |
# 迭代法
层序遍历,但找到左右都为空的节点时直接返回深度。
class Solution { | |
public: | |
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { | |
if (root == nullptr) return 0; | |
int depth = 0; | |
queue<TreeNode*> que; | |
que.push(root); | |
while(!que.empty()) { | |
int size = que.size(); | |
depth++; // 记录最小深度 | |
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { | |
TreeNode* node = que.front(); | |
que.pop(); | |
if (node->left) que.push(node->left); | |
if (node->right) que.push(node->right); | |
if (!node->left && !node->right) { // 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出 | |
return depth; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return depth; | |
} | |
}; |