# 栈与队列理论基础
队列是先进先出,栈是先进后出。
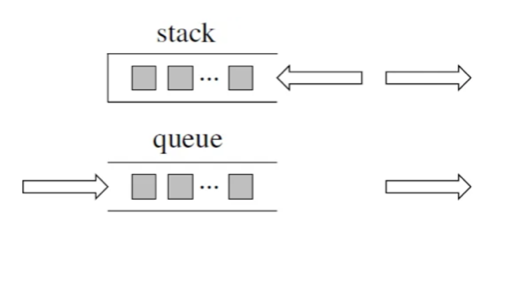
栈提供 push 和 pop 等接口,所有元素必须符合先进后出的规则,所以栈不提供走访功能和迭代器。
栈以底层容器来完成所有工作,对外统一接口,底层容器是可插拔的。
因此在 STL 中栈汪汪不被归为容器 (container),而被归为容器适配器 (container adapter)。
栈的底层实现可以是 vector , deque , list 等数组和链表的底层实现。
常用的 SGI STL 如果没有指定底层实现,默认是以 deque 为底层数据结构。
deque 是一个双向队列,只要封住一段,开通一段就可以实现栈的逻辑。
队列和栈的特性是基本一致的,同样不允许有遍历行为,不提供迭代器,SGI STL 中队列一样以 deque 为缺省情况下的底层数据结构。
# 用栈实现队列
题目链接🔗
使用栈来模拟队列需要用到两个栈,一个输出栈,一个输入栈。

- push (): 直接将数据放入输出栈。
- pop (): 如果输出栈为空,将输入栈所有元素全部移入。如果不为空直接从输出栈移出数据。
- peek (): 输出栈的 top (),因为和 pop () 功能类似,直接调用。
- empty (): 输入和输出栈都为空,队列为空。
class MyQueue { | |
private: | |
stack<int> stIn; | |
stack<int> stOut; | |
public: | |
MyQueue() {} | |
void push(int x) { | |
stIn.push(x); | |
} | |
int pop() { | |
// 输出栈为空,移入输入栈所有数据 | |
if(stOut.empty()){ | |
while(!stIn.empty()) { | |
stOut.push(stIn.top()); | |
stIn.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
int tmp = stOut.top(); | |
stOut.pop(); | |
return tmp; | |
} | |
int peek() { | |
int tmp = this->pop(); // 调用已有的 pop () | |
stOut.push(tmp); // 弹出了要再添加回去 | |
return tmp; | |
} | |
bool empty() { | |
return stIn.empty() && stOut.empty(); | |
} | |
}; |
# 用队列实现栈
题目链接🔗
# 两个队列实现栈
队列是先进先出的规则,把一个队列元素移入另一个队列,数据的顺序没有改变。

两个队列中有一个队列的作用是备份。que1 队列中除最后一个元素以外的所有元素全部移入 que2,弹出 que1 最后的元素,再将 que2 的元素全部移回 que1
class MyStack { | |
public: | |
queue<int> que1; | |
queue<int> que2; // 辅助队列,用来备份 | |
/** Initialize your data structure here. */ | |
MyStack() {} | |
/** Push element x onto stack. */ | |
void push(int x) { | |
que1.push(x); | |
} | |
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ | |
int pop() { | |
int size = que1.size(); | |
size--; | |
while (size--) { // 将 que1 导入 que2,但要留下最后一个元素 | |
que2.push(que1.front()); | |
que1.pop(); | |
} | |
int result = que1.front(); // 留下的最后一个元素就是要返回的值 | |
que1.pop(); | |
que1 = que2; // 再将 que2 赋值给 que1 | |
while (!que2.empty()) { // 清空 que2 | |
que2.pop(); | |
} | |
return result; | |
} | |
/** Get the top element. */ | |
int top() { | |
return que1.back(); | |
} | |
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ | |
bool empty() { | |
return que1.empty(); | |
} | |
}; |
# 优化:一个队列实现栈
一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外)重新添加到队列尾部,此时再去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
class MyStack { | |
public: | |
queue<int> que; | |
/** Initialize your data structure here. */ | |
MyStack() { | |
} | |
/** Push element x onto stack. */ | |
void push(int x) { | |
que.push(x); | |
} | |
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ | |
int pop() { | |
int size = que.size(); | |
size--; | |
while (size--) { // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部 | |
que.push(que.front()); | |
que.pop(); | |
} | |
int result = que.front(); // 此时弹出的元素顺序就是栈的顺序了 | |
que.pop(); | |
return result; | |
} | |
/** Get the top element. */ | |
int top() { | |
return que.back(); | |
} | |
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ | |
bool empty() { | |
return que.empty(); | |
} | |
}; |
# 有效的括号
题目链接🔗
括号匹配是栈的经典题目。
首先分析一下几种不匹配的情况:
- 字符串里左方向的括号多余
- 字符串里没有括号多余,但括号类型没有匹配上
- 字符串里右方向的括号多余
只要代码覆盖三种不匹配的情况,基本不会出现问题。

- 第一种情况:已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以
return false - 第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有要匹配的字符。所以
return false - 第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号
return false
当字符串遍历完之后,栈是空的,就说明全都匹配了。
class Solution { | |
public: | |
bool isValid(string s) { | |
if (s.size() % 2 != 0) return false; // 如果 s 的长度为奇数,一定不符合要求 | |
stack<char> st; | |
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { | |
if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')'); | |
else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}'); | |
else if (s[i] == '[') st.push(']'); | |
// 第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号 return false | |
// 第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有我们要匹配的字符。所以 return false | |
else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i]) return false; | |
else st.pop(); //st.top () 与 s [i] 相等,栈弹出元素 | |
} | |
// 第一种情况:此时我们已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以 return false,否则就 return true | |
return st.empty(); | |
} | |
}; |
在匹配左括号的时候,右括号先入栈,就只需要比较当前元素和栈顶相不相等就可以了,比左括号先入栈代码实现要简单